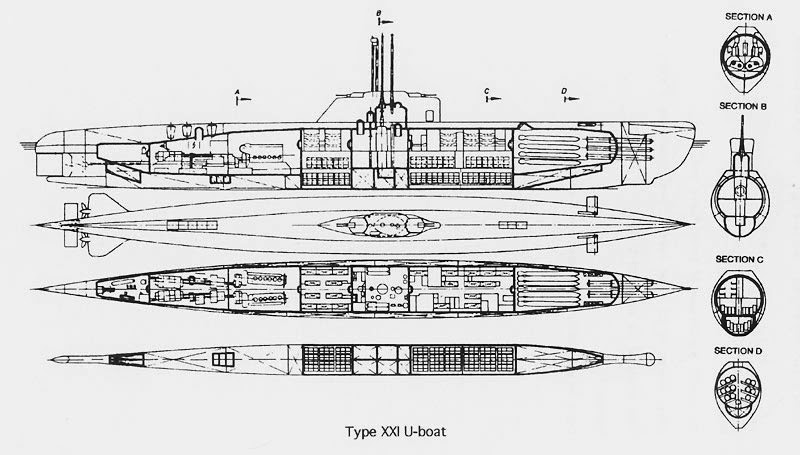
Diagram of a Type XXI.
---
The evolution of postwar German designed submarines - starting with the HDW 201 at the bottom of the diagram.
This study of German submarine developments is a work in progress which is extending from the immediate post World War Two era - through the 1960s launch of HDW Type 205s - to the July 2014 TKMS efforts to sell between 6 and 12 large SSKs to Australia.
Allied Derivatives of the German Type XXI
At the end of WWII the victorious allies benefited from Germany’s advanced U-boat developments which reached the most useful state of development in the Type XXI U-boat. The XXI's much higher battery capacity and snorkel resulted in a far lower “indiscretion [unsafe operating] ratio” and streamlined hull all allowed faster, longer duration and quieter submerged operation.
XXI designs influenced post-war submarines, including the:
- US GUPPY (greater underwater propulsion power program) improvements to the US Gato, Balao, and Tench class submarines;
- Chinese built Romeo class submarines based on the XXI design via Soviet-supplied designs. The Ming class, is based on the Romeo design. Some Mings are still in operation in the PLA-Navy 2013 (2 Mings are being transferred to Bangladesh).
- UK Porpoise and Oberon classes,
- France, the XXI ex-U 2518 became French submarine Roland Morillot The XXI design influence the French Arethuse and Daphne classes, and
- Sweden’s Hajen class (built 1954-58) was also influenced by the XXIs.
Postwar Air Independent Propulsion (AIP)
Two German WWII internal oxygen supply AIP developments were tested by some victorious allies after WWII. But proved too problematic to be adopted. These technologies included the:
- Walter engine - hydrogen peroxide is used as a source of oxygen to burn diesel driving steam turbines. An article translated from German providing more detail on the Walter Drive (engine) is here. This technology proved too volatile and explosive to be safe, and
- closed cycle diesel engines - uses a submarine diesel engine which can be operated conventionally on the surface, but which can also be provided with oxidant, stored as liquid oxygen,. Considered dangerously explosive from fire, heat or sparks.
Postwar Transition
Between May 1945 and 1956 former members of the Kriegsmarine formed the nucleus of the German Mine Sweeping Administration amounting to a transition stage for the navy. In 1956, with West Germany's accession to NATO, the West German Navy, colloquially known as Bundesmarine (Federal Navy?) was established. In 1956 East Germany formed the Volksmarine ("People's Navy").
Submarines ("U-Boots") were (still are?) built at HDW dockyards at Kiel and Hamburg.
Submarines ("U-Boots") were (still are?) built at HDW dockyards at Kiel and Hamburg.
The HDW Type 201
From around 1957 West German facilities to develop and construct submarines had been repaired, rebuilt or built. This included dockyards which had been destroyed by bombing in the war.
In West Germany The HDW 201s, launched in 1962, were Germany's first class of military submarines built after World War II.
Functions - They were designed to defend coastal (or littoral) Baltic-North Sea areas and therefore could be very light in displacement (350 tonnes surfaced and 450 tonnes submerged) with a total of 8 torpedoes or 16 sea mines
They were built out of a magnetic steel to counter the threat of magnetic naval mines, but this steel had been insufficiently tested and proved to be problematic in service with the Bundesmarine. Microscopic cracks in the pressure hull forced the cancellation of 9 of the 12 ordered submarines and the early retirement of the three completed boats. This led to the need for the Type 205s.
Type 205
205s mainly differed from the 201s in hull steel used. Various steels were tried in different 205 hulls. The most acceptable steel was found to be PN 18 S2, which was developed by the steel company Phoenix Rheinrohr . PN 18 S2 (is ST-52 the same steel?) has been used for all subsequent submarines for the German Navy up to Type 212A .
The Type 205s were launched from 1962 to 1968 and operational between 1967 and 2004. The last 205 in service was U 12 eventually used as a test bed for new weapons systems until its retirement in June 2005.
Functions - Up until the fall of the Berlin Wall (1989) major peacetime functions most probably included providing a deterrent and electronic and special forces intelligence gathering missions against Warsaw Pact countries. If war broke out the 205's main function was to operate within the NATO structure specifically to defend against Warsaw Pact landing ships and other naval vessels threatening the Baltic and North Seas.
Wikipedia-English sources used so far
Functions - They were designed to defend coastal (or littoral) Baltic-North Sea areas and therefore could be very light in displacement (350 tonnes surfaced and 450 tonnes submerged) with a total of 8 torpedoes or 16 sea mines
They were built out of a magnetic steel to counter the threat of magnetic naval mines, but this steel had been insufficiently tested and proved to be problematic in service with the Bundesmarine. Microscopic cracks in the pressure hull forced the cancellation of 9 of the 12 ordered submarines and the early retirement of the three completed boats. This led to the need for the Type 205s.
Type 205
205s mainly differed from the 201s in hull steel used. Various steels were tried in different 205 hulls. The most acceptable steel was found to be PN 18 S2, which was developed by the steel company Phoenix Rheinrohr . PN 18 S2 (is ST-52 the same steel?) has been used for all subsequent submarines for the German Navy up to Type 212A .
The Type 205s were launched from 1962 to 1968 and operational between 1967 and 2004. The last 205 in service was U 12 eventually used as a test bed for new weapons systems until its retirement in June 2005.
Functions - Up until the fall of the Berlin Wall (1989) major peacetime functions most probably included providing a deterrent and electronic and special forces intelligence gathering missions against Warsaw Pact countries. If war broke out the 205's main function was to operate within the NATO structure specifically to defend against Warsaw Pact landing ships and other naval vessels threatening the Baltic and North Seas.
Wikipedia-English sources used so far
Wikipedia-German sources being used
Thankyou MHalblaub for drawing my attention to Wikipedia-German and other websites translated into English which have much more detail on German submarine matters :-)
[The shipyard HDW has his own ideas to a more advanced version called class 216 presented, which should have a greater range and a longer operating lifetime of a compared to the 212 Class almost 40 percent larger boat length. [18] Potential buyers of the 4000-t- Boats Australia could be that looking for a replacement for the submarines of the Collins-class is. [19] The submarines have 33 people crew. Instead of the outdated lead-acid batteries of any ancestors are here lithium-ion batteries can be used. [20]reference to 218SG]
Other German sources being used
http://www.die-marine.de/_deutsch/schiffe/subm.htmThe U-boat Arm of the German Navy
http://seefahrer.blog.de/tags/uboot/ Seafarer or Sailor blog
http://seefahrer.blog.de/tags/uboot/ Seafarer or Sailor blog
Pete